The main cause of acute knee pain in patients over 50 years of age is gonarthrosis (deforming arthrosis of the knee joint).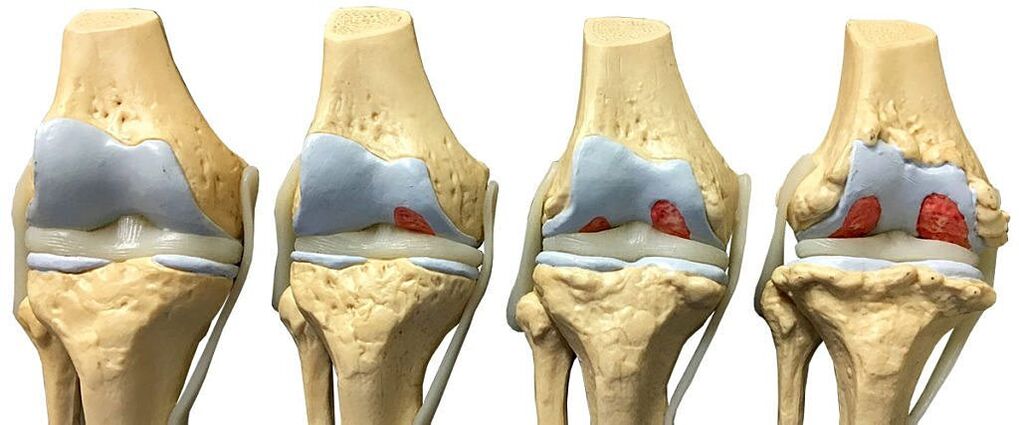 The disease is characterized by rapid progression and can lead to disability and disability. Therefore, timely detection of symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint and treatment of the disease, including at home, are the main tasks when examining patients at risk for pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
The disease is characterized by rapid progression and can lead to disability and disability. Therefore, timely detection of symptoms of arthrosis of the knee joint and treatment of the disease, including at home, are the main tasks when examining patients at risk for pathologies of the musculoskeletal system.
What is knee osteoarthritis
The knee joint is one of the most mobile joints in the human skeleton and is prone to injury and other mechanical damage. It connects the tibia and femur, as well as the largest sesame bone, located in the tendons of the quadriceps femoris (patella or patella). The surfaces of the joint are covered with cartilage tissue - a dense, elastic substance that surrounds chondrocytes (oval cells formed from chondroblasts), forming a protective covering around them and also acting as a shock absorber.
The composition of cartilage includes collagen - a fibrillar protein, which is the main element of connective fibers and gives strength and elasticity to cartilage - and glucosamine. Glucosamine is a substance produced by cartilage. Glucosamine is part of the synovial fluid - a yellowish elastic mass that fills the joint cavity and acts as a lubricant. When the synthesis of glucosamine and proteoglycans is disturbed, the amount of synovial fluid decreases, which leads to the exposure of parts of the joint and the appearance of severe pain, therefore, the treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint of the 1st degree always includes the use of chondroprotective drugs.
What happens in the joints in osteoarthritis:
- the cartilage becomes soft and loose, and deep ulcers appear on its surface;
- the synovial membrane thickens;
- the composition of the synovial fluid changes, its secretion decreases;
- there is a sprain of the ligaments and joint capsule;
- The joint cavity is filled with exudate - an inflammatory fluid released from blood vessels during an acute period of inflammation.
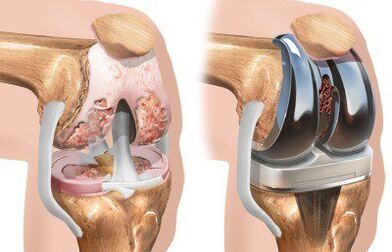
In the absence of timely and adequate treatment, arthrosis leads to complete deformation and destruction of the knee joint, while the patient can show both unnatural mobility and complete immobility of the joint. In order to stop the process of destruction of the joint and cartilage surface in case of diagnosed arthrosis of the knee, the doctor may suggest arthroplasty - a surgical intervention in which the damaged joint is replaced with an artificial prosthesis of a suitable size.
Primary knee arthroplasty costs vary by region and can range from $255 to $1465.
If indicated, the operation can be performed according to the quota within the CHI program.
Classification and etiological factors
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint can be primary and secondary. Primary arthrosis is diagnosed in cases where it is impossible to accurately determine the cause of the pathology. If cartilage deformation was preceded by other diseases and pathologies, knee injuries, then arthrosis is considered secondary, that is, developing against the background of a primary disease.
The main causes of secondary osteoarthritis of the knee joints include:
- various dysplasias and other pathologies in which abnormal development and formation of tissues occurs;
- neurodystrophic diseases of the lumbar or cervical spine;
- inflammation of the knee joint (arthritis);
- Injuries and microtraumas of the joint;
- surgical removal of a damaged meniscus or part of it (meniscectomy);
- Diseases of the endocrine system and hormonal disorders, in which the rate of metabolic reactions slows down, metabolism in bone tissue is disturbed.
Primary arthrosis of the knee joint often develops in people leading a sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, regularly subjected to increased physical activity in the knee joint. Obese patients, people over 50 years old, residents of environmentally disadvantaged areas, patients with various types of toxic addictions (smokers, drug addicts, alcoholics) are also at increased risk of developing gonarthrosis.
Regular hypothermia can contribute to inflammation and further deformation of the knee joint, therefore, people with a tendency to diseases of the musculoskeletal system are recommended to observe the temperature regime and stop activities associated with prolonged exposure to low temperatures (work outdoors, in refrigerated andfreezers). etc. ) d. ).
Women over 45 who are interested in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis should know that a provoking factor in the development of the pathology can be reduced estrogen synthesis, which can occur after menopause and with some gynecological diseases: endometrial hyperplasia, uterine myoma, fibroadenoma, endometriosis. Also, a negative factor are various diets that limit the intake of foods rich in minerals, vitamins and other elements necessary for joint health.
signs and symptoms
So that the prognosis for later life is as favorable as possible, it is important not only to know how to treat osteoarthritis of the knee, but also what the symptoms of the disease are. This is necessary in order to see a specialist in good time and to identify possible malpositions and other injuries of the knee joint at an early stage. At the initial stage, the pathology has rather meager symptoms, therefore it is possible to detect arthrosis of the knee of the 1st degree only after conducting hardware and instrumental diagnostics.
The first symptoms of the disease are:
- morning stiffness in knee;
- pain when walking when walking a distance of more than 1-1. 5 km;
- pain in the knees when sitting for a long time (more than 2 hours in a row);
- pain in the knee joint after standing for a long time;
- Pain in the knees that occurs at the end of the day or in the first half of the night's sleep.
If the patient does not receive the necessary treatment at this stage, the disease will progress. In order to choose the right drug for arthrosis of the knee joint, it is necessary to undergo a number of diagnostic examinations (MRI, computed tomography, radiography, etc. ) and determine the degree of deformation, the level of synovial fluid in the joint cavity, the density of thecartilage and synovial membrane. Symptoms of arthrosis of the knees 2 and 3 degrees are shown in the table below.
| diagnostic sign | Osteoarthritis of the knee 2 degrees | Osteoarthritis of the knee 3 degrees |
|---|---|---|
| Pain when resting at night | May occur when changing body position or getting out of bed. | Performs without moving. |
| Use of public transport (without low-floor buses) | The patient has pain when climbing stairs, but can use public transport without assistance with certain limitations. | Due to the limited mobility of the knee joint, the patient cannot board the bus or train alone. |
| lameness | Easily put. | Lameness is severe, additional supports (sticks) are required for movement. |
| Stiffness in knee after waking up | Takes less than 10-15 minutes. | Takes about 20-30 minutes or more. |
| pain when walking | Occurrence after passing 800-1000 m. | They start at the beginning of the movement and intensify after a distance of less than 500 m. |
| Self-Service Capability | Usually saved. | The patient cannot perform a number of actions without outside help. |
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint at home
Treatment of arthrosis of the knee joint can be carried out with the help of:
- medical methods;
- physiotherapeutic exercises;
- Massage.
The use of traditional drug formulations is only possible after consultation with the attending physician and is not intended to replace the main treatment prescribed by a specialist.
The choice of drugs and methods of treatment depends not only on the age of the patient and his chronic diseases, but also on the stage of arthrosis and the degree of deformation of the cartilage and joint surface.
Osteoarthritis 1 degree
This is the mildest form of arthrosis, which in most cases can be cured with minor medication and additional measures: massage, exercise therapy, physiotherapy. The most effective treatment for knee osteoarthritis, regardless of its stage, is laser therapy. This is the main method of physiotherapy, which gives quite good results in the initial stages of arthrosis.
It helps to achieve the following effect:
- the degree of inflammation in the articular cavity decreases;
- the intensity of pain decreases;
- the process of tissue regeneration is stimulated;
- the need for the use of glucocorticosteroids and other drugs with serious side effects disappears.
As an alternative to laser therapy, the doctor may offer pulse magnetotherapy, acupuncture, electromyostimulation, and electrophoresis.
All of these methods are very effective in treating osteoarthritis.with a degree of deformation of not more than 20-25%, but the effectiveness of treatment will be higher if it is combined with physiotherapy exercises and massage.
Orthopedists and surgeons notice the positive effect of water exercises on developing muscle strength in the legs.
Patients with arthrosis of the knees of 1-2 degrees can be offered sanatorium treatment (during a period of stable remission), including mud therapy, warming up in a sauna, therapeutic baths. A special diet is prescribed for overweight patients, since obesity is one of the main factors in the development of osteoarthritis of the knee joint.
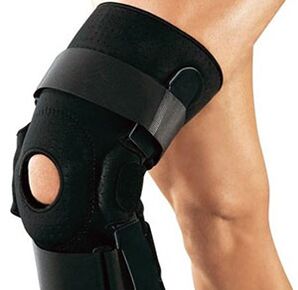
Osteoarthritis 2 degrees
Treatment of second-degree knee arthrosis includes physiotherapy and massage (outside the acute phase), special nutrition, physiotherapy exercises and medication. It is very important to reduce the load on the damaged joint: limit walking, avoid movements that require knee flexion. In the case of rapidly progressing arthrosis, the use of special orthoses is indicated - orthopedic aids intended to fix the diseased joint and limit its mobility.
The drug treatment regimen may include the following drugs:
- chondroprotectors;
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid;
- Injections of glucocorticosteroid hormones.
The diet of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee should include a sufficient amount of foods rich in collagen.
The:
- products with gelling additives (jelly, jelly, jelly, aspic);
- products with added pectin;
- fish oil.
Almost all fruits and berries contain essential amino acids and minerals to keep joints healthy and flexible, but these foods should be consumedrestricted in diabetics.
Osteoarthritis 3 degrees
The treatment of grade 3 knee arthrosis does not differ from the treatment of grade 2 arthrosis.
With its ineffectiveness and severe limitation of movement, the patient is prescribed surgical treatment with further prosthetics of the damaged joint.
folk methods
Before you learn how to treat knee joints at home with recipes of alternative medicine, you need to consult a doctor. The use of the methods listed below is only permitted in the case of arthrosis of the first degree and in the early stages of arthrosis of the second degree.
Nettle and lemon infusion
This infusion should be taken orally 20-30 minutes before meals. A single dose is 50-80 ml.
To prepare the infusion you must:
- Mix 100 g of dried or fresh nettle leaves with three peeled garlic cloves;
- pass the mixture through a meat grinder;
- add 4 tablespoons of lemon juice;
- mix everything, add 250 ml of boiling water and cover;
- insist 4 hours.
The duration of treatment in this way is at least 60 days. In the first week, the infusion should be taken 1 time per day, in the next 7-10 days - 2 times a day. From the third week of treatment, the number of doses should be increased to 3 times a day.
Honey ointment for joints
This ointment helps reduce inflammation and reduce pain. The first result is noticeable after a week of daily use, but to get a stable result you need to use it for 30-45 days.
To prepare the ointment you must:
- Melt 2 tablespoons of butter;
- Mix the oil with two spoons of honey and one spoon of apple cider vinegar 6%;
- Place the mixture in the fridge to set.
Apply such an ointment to your knees 2-3 times a day (the last time - before bedtime).
Bath with dandelions
For such a bath, a tincture of dandelion roots is used. To prepare it, you need to mix 120 g of crushed dandelion roots with 150 ml of vodka and insist a day in a dark place. Before bathing, the contents of the container must be poured into water and stirred. It is recommended to take such a bath 1-2 times a week. After the procedure, the pain in the knees will decrease and the mobility of the joints will gradually be restored. The effectiveness of the treatment will be higher if you add 150 g of sea salt enriched with iodine and bromine to the water.
reviews
- "Only injections of hyaluronic acid have helped me with arthrosis. A very good drug with a minimum of side effects and high efficiency. Now I have almost no knee pain, although before I could not even walk down the stairs without help. "
- "It seems to me that osteoarthritis of the knee is a disease that cannot be cured by anything. You can dull the pain a little, but then it still comes back. With exacerbations, I am treated with ficus and Jerusalem artichoke. It helps no worse than pills, only the heart and liver are not damaged.
- "I was also diagnosed with second-degree osteoarthritis of the knee. Most likely, the reason was overweight (at that time I weighed more than 130 kg). A salt-free diet, chondroprotectors, anti-inflammatory ointments and hormone injections were prescribed for treatment. I did everything according to the instructions - arthrosis was completely gone.
Osteoarthritis of the knee joint is a serious pathology of the musculoskeletal system, prone to rapid progression. The treatment regimen should be selected by the attending physician after a comprehensive diagnosis and determination of the degree of degenerative, dystrophic processes and deformations of the cartilage and articular surface. The prognosis of treatment depends on compliance with doctor's prescriptions and timely seeking medical help.





















